Key Principles for Selecting Addressable LED Strip Controllers
Understanding Addressable LED Strips
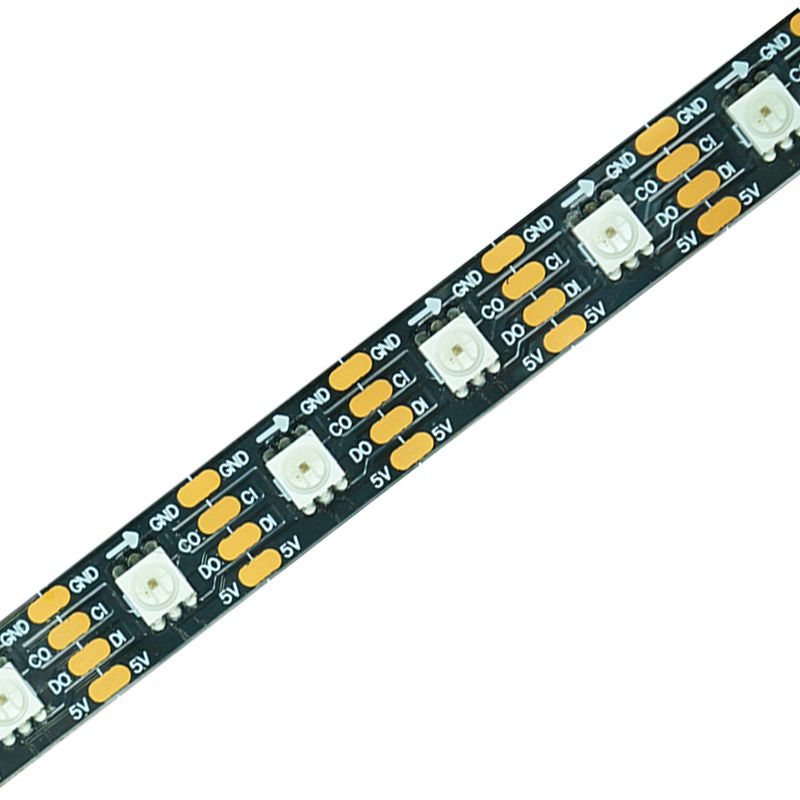
Addressable LED strips, also known as digital LED strips or LED strips with IC, are LED strips equipped with an integrated circuit (IC) that allows individual or grouped control of LEDs. These strips can produce complex lighting effects like flowing, chasing, gradient, and flashing.
Types of Addressable LED Strips
1.Based on Communication Protocol
SPI Protocol: SPI-based addressable LED strips communicate using a clock and data line for precise and high-speed data transfer.
DMX Protocol: DMX-based LED strips adhere to the DMX512 protocol, commonly used for professional-grade lighting applications, such as stage lighting.
2.Based on IC Model
Features:
- Integrated SPI protocol.
- Each LED has an embedded RGB chip and IC, enabling per-LED control.
- No breakpoint transmission (data loss in one LED does not affect the others).
Voltage:Typically 5V.
Advantages:High cost-effectiveness, easy control.
Applications:DIY projects, signage, decorative lighting, home decor.
Features:Dual-line control (clock line + data line) for higher data transfer rates and smoother animations.
Voltage:5V
Advantages:Higher refresh rates and precise control compared to WS2812. Ideal for fast dynamic changes.
Applications:High frame-rate LED displays, complex dynamic lighting projects.
Features:
- External chip control with 3-line communication (power, ground, data).
- Controls groups of LEDs rather than individual LEDs.
Voltage:12V
Advantages:Suitable for long-distance installations and larger projects with simpler effects.
Applications:Building lighting, outdoor advertisements, ambient lighting.
Features:Similar to APA102 with dual-line control. Provides high refresh rates and precise pixel control.
Voltage:5V
Advantages:APA102-compatible with better interference resistance, ideal for long-distance control.
Applications: Complex dynamic lighting, large LED displays, architectural decoration
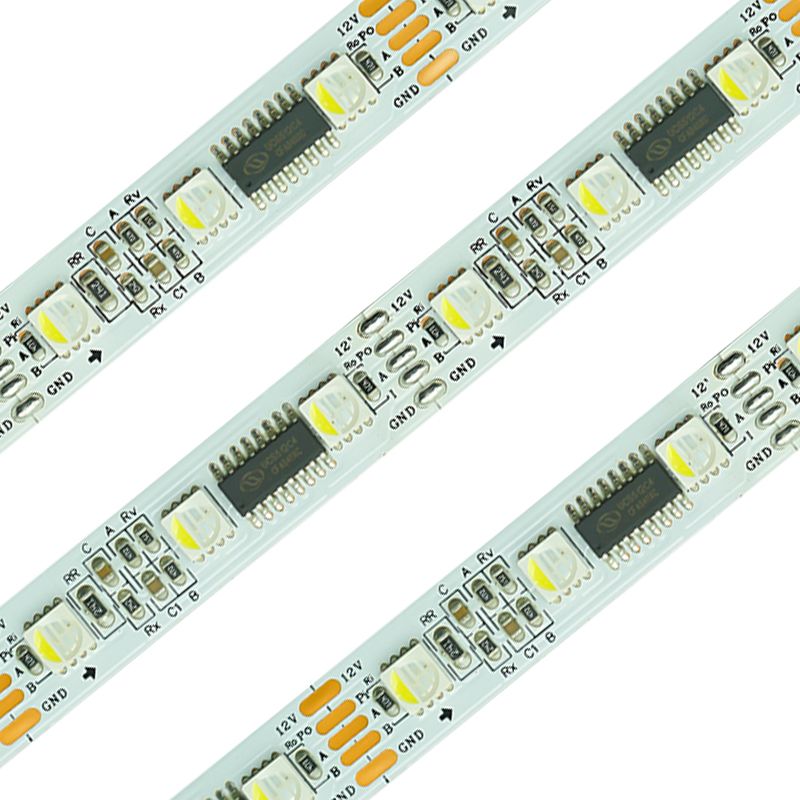
Features:3-line control, similar to WS2811, supports grouped control of LEDs.
Voltage: Typically 12V or 24V.
Advantages:Long-distance compatibility, outdoor project suitability.
Applications:Building outlines, outdoor advertising, landscape lighting.
Features:DMX512 protocol for precise control over each LED.
Voltage:12V or 24V.
Advantages:Complex and precise lighting control for professional-grade projects.
Applications:Stage lighting, large architectural lighting, entertainment facilities.
Features:Built-in constant current IC ensures consistent brightness and color across long strips.
Voltage:12V
Advantages:Stable voltage performance, ideal for long-distance installations.
Applications:Large-scale architectural lighting, outdoor decorations.
Features:Built-in constant current IC, RGB control.
Voltage:24V, individual pixel control..
Advantages:24V individual pixel control, rare in the market.
Applications:Gaming equipment, home appliance ambient lighting, smart home lighting.
By understanding the characteristics, advantages, and applications of these different addressable LED strips, you can choose the right solution for your specific lighting project. Whether for DIY, professional-grade stage lighting, or large-scale architectural installations, there's an option tailored to your needs.
Basic Principles for Choosing an Addressable LED Strip Controller
1.Select the best controller based on the LED strip required for the project, with communication protocols: SPI or DMX
Currently, the mainstream control protocols for addressable LED strips on the market are SPI and DMX. SPI stands for “Serial Peripheral Interface”, a synchronous serial interface technology introduced by Motorola.
The communication principle of SPI is simple, operating in a master-slave mode. Addressable LED chips are representative products developed based on the SPI protocol. Four-wire (VDD, DATA, CLOCK, GND) products include HD107S, SK9822, APA102 etc. These products feature fast data transmission speed, high PWM refresh rate, and excellent performance. In addition, we have developed lower-cost three-wire transmission products (integrating data and clock signals), such as SK6812, WS2812B, external WS2811, and UCS1903. On the basis of three-wire transmission, products with “breakpoint-resume” functionality have also been developed.
“Breakpoint-resume” means that if a single LED fails, it does not affect the subsequent LEDs from receiving the signal. These designs use a dual-signal line for main and backup transmission, with representative products including WS2815B, WS2813B, SK6813, external WS2818B, and LB1934A.
Before selecting a suitable controller, you need to know which signal type the addressable LED strip IC uses.
For addressable LED strip controllers using the DMX512 signal, whether single-port, 4-port, or 8-port, it is recommended to control within 300 pixels per port.For addressable LED strip controllers using the SPI signal, it is recommended that a single-port controller controls within 1,500 pixels, while for 4- or 8-port controllers, each port should control about 600 pixels.
For an 8-port controller required for the project, if the number of controllers does not exceed 3, it is recommended to use a standard offline controller.If the number of controllers exceeds 3, it is recommended to use a master–slave control mode with single-port offline controllers, keeping the total number of pixels within 2,048 per controller.
It is important to note that the number of “pixels” refers to the number of “addressable pixels”, not the number of LEDs.
For example, a 5V addressable LED strip is typically one LED per pixel, meaning 60 LEDs equal 60 pixels. A 12V addressable LED strip may be one LED per pixel or three LEDs per pixel.
Taking an LED strip with 60 LEDs per meter as an example, there is a difference between 60 pixels and 20 pixels. Before selecting a controller, it is necessary to know the pixel count in order to calculate the appropriate multi-port controller.
Depending on the control method, the program effects will vary with the frequency.
When selecting a controller, you should consider whether a computer connection is required—this determines whether to choose an online or offline controller.
If the project requires frequent changes to lighting effects and involves multiple controllers, it is recommended to use a SD card (plug-in) controller or an online controller in master–slave mode. If the project only needs to run fixed programs with simple control, an SD card controller or a basic controller can be used.
Based on the project, consider the minimum control unit of the LED strip
Some projects may involve a small number of LED strips but with a very scattered distribution.To avoid signal loss due to long distances, it is necessary to equip additional controllers according to the number of distributed sections, beyond the basic quantity of LED strips.
Based on whether the client requires connection to other control systems. For example, if the project needs to be controlled by Madrix software, the corresponding controller must be provided.The above four principles should be considered together, not separately, to determine the most suitable controller mode for different functional requirements.
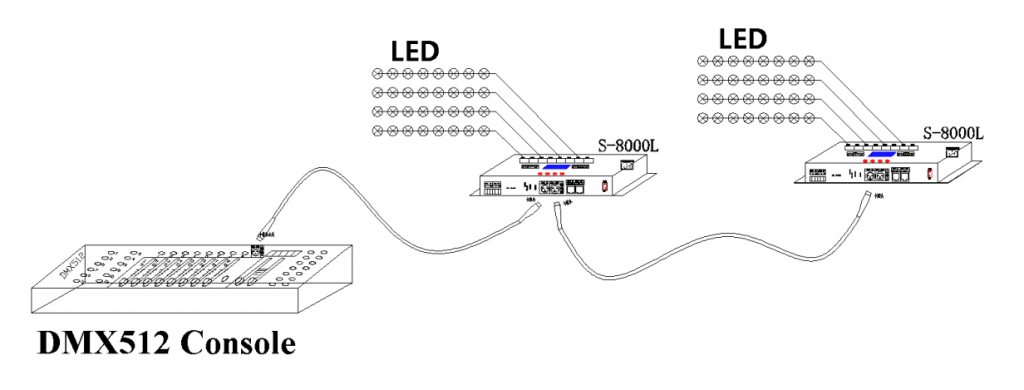
1. Docking Console Control Mode: S-8000L can synchronize multiple SD card controllers without a master controller.

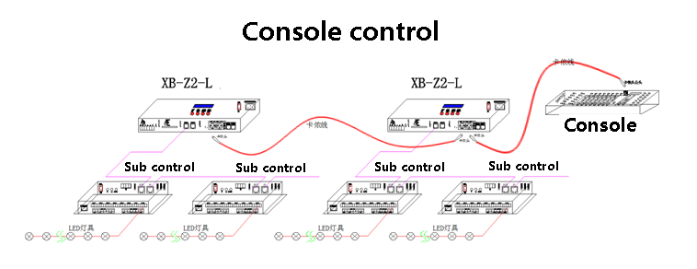
Console Master + Sub-Controller Mode: XB-Z2-L master controller + T-790K sub-controller, with the master controller equipped with an SD card and the sub-controller operating without an SD card.
2. Controller for Connection with Madrix Online Software
T-790K (Madrix version) – available in 8-port or single-port models, supporting up to 510 SPI pixels.It is generally not recommended to use Madrix to control 512 LED strips, as the controllable pixel count is low—only about 170 pixels per port.

4. Universal Offline Controller
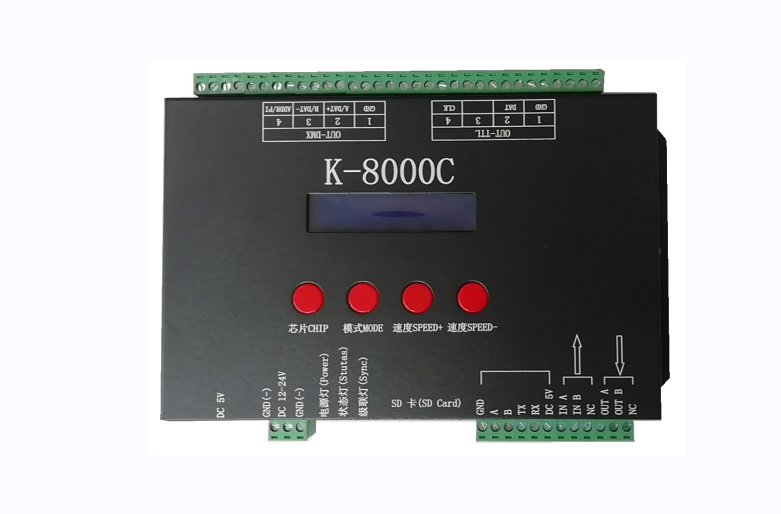
K-1000C (with code-writing function): Single-port controller that supports up to 1,536 pixels for SPI signal ICs and 300 pixels for DMX512 ICs. Can synchronize with multiple unitsK-8000C (with code-writing function): Eight-port controller, each port supporting up to 800 pixels for SPI signal ICs and 300 pixels for DMX512 ICs. Can synchronize with multiple units.


5. Offline Master–Slave Controller

XB-809-A touch screen master controller
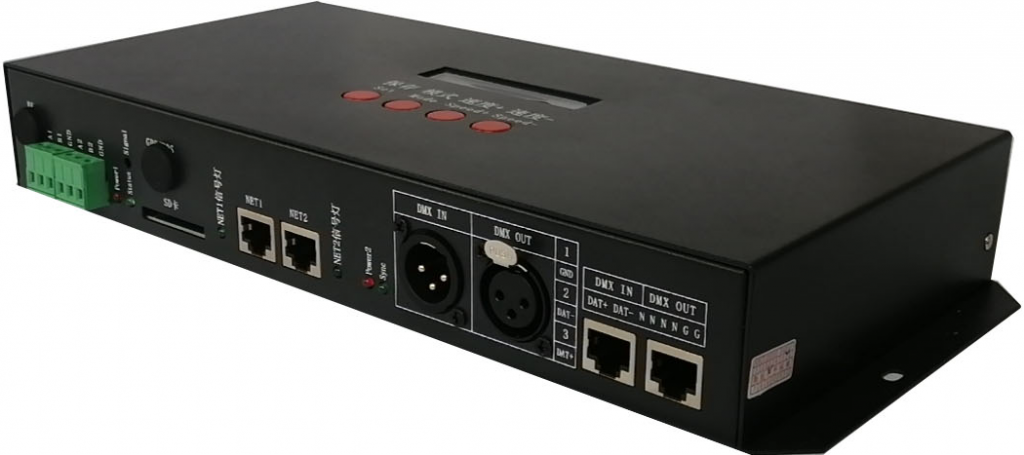

XB-Z2-L console master controller

Sub-controller T-790K
Engineering Cases
With over 13 years of sales experience, we have assisted clients worldwide in selecting the most suitable controllers for their addressable LED strip projects. Below are some real-life examples:
Digital Led Strip Color Changing Lights
Arduino SK6812 Individually addressable rgbw led strip
Customer Case Addressable RGB COB LED Strip Lightig Effects, Spotless & Continuous Light
Application effect of outdoor neon light strips (customer case)
Outdoor neon light belt installation effect display
Flexible Neon Tube Installation - LED Neon Strips
If you have any questions about selecting the right controller for your addressable LED strip, please feel free to contact us. We are here to provide professional guidance and support for your lighting projects.